-
SOTA
-
Accelerator Toolkit
-
Deep Learning Toolkit
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AlphaDropout
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- ELU
- Exponential
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- GELU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- HardSigmoid
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- Multiply
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- PReLU
- ReLU
- SELU
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Sigmoid
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- Split
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- Substract
- Show All Articles (63) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Exp
- Identity
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- lrfft
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- Shape
- SequenceLength
- Shrink
- Sin
- Sign
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- lslnf
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- Show All Articles (65) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- ConvInteger
- Conv
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Sinh
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLinear
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- LSTM
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- MutiHeadAttention
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- MultiHeadAttention
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (22) Collapse Articles
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Bidirectional
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dense
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- MultiHeadAttention
- LSTM
- PReLU 5D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (21) Collapse Articles
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MultiHeadAttention
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Resume
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- PReLU 4D
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Resume
- Show All Articles (27) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- BatchNormalization
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Computer Vision Toolkit
-
CUDA Toolkit
-
- Resume
- Array size
- Index Array
- Replace Subset
- Insert Into Array
- Delete From Array
- Initialize Array
- Build Array
- Concatenate Array
- Array Subset
- Min & Max
- Reshape Array
- Short Array
- Reverse 1D array
- Shuffle array
- Search In Array
- Split 1D Array
- Split 2D Array
- Rotate 1D Array
- Increment Array Element
- Decrement Array Element
- Interpolate 1D Array
- Threshold 1D Array
- Interleave 1D Array
- Decimate 1D Array
- Transpose Array
- Remove Duplicate From 1D Array
- Show All Articles (11) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- Substract
- Multiply
- Divide
- Quotient & Remainder
- Increment
- Decrement
- Add Array Element
- Multiply Array Element
- Absolute
- Round To Nearest
- Round Toward -Infinity
- Round Toward +Infinity
- Scale By Power Of Two
- Square Root
- Square
- Negate
- Reciprocal
- Sign
- Show All Articles (4) Collapse Articles
StringSplit
Description
StringSplit splits a string tensor’s elements into substrings based on a delimiter attribute and a maxsplit attribute.
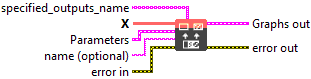
The first output of this operator is a tensor of strings representing the substrings from splitting each input string on the delimiter substring. This tensor has one additional rank compared to the input tensor in order to store the substrings for each input element (where the input tensor is not empty). Note that, in order to ensure the same number of elements are present in the final dimension, this tensor will pad empty strings as illustrated in the examples below. Consecutive delimiters are not grouped together and are deemed to delimit empty strings, except if the delimiter is unspecified or is the empty string (“”). In the case where the delimiter is unspecified or the empty string, consecutive whitespace characters are regarded as a single separator and leading or trailing whitespace is removed in the output.
The second output tensor represents the number of substrings generated. maxsplit can be used to limit the number of splits performed – after the maxsplitth split if the string is not fully split, the trailing suffix of input string after the final split point is also added. For elements where fewer splits are possible than specified in maxsplit, it has no effect.
Input parameters
![]() specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
![]() X (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, tensor of strings to split.
X (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, tensor of strings to split.
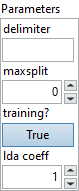
![]() delimiter : string, delimiter to split on. If left unset or set to the empty string (“”), the input is split on consecutive whitespace.
delimiter : string, delimiter to split on. If left unset or set to the empty string (“”), the input is split on consecutive whitespace.
![]() maxsplit : integer, maximum number of splits (from left to right). If left unset (or if the number of possible splits are less than maxsplit), it will make as many splits as possible. Note that the maximum possible number of substrings returned with
maxsplit : integer, maximum number of splits (from left to right). If left unset (or if the number of possible splits are less than maxsplit), it will make as many splits as possible. Note that the maximum possible number of substrings returned with maxsplit specified is maxsplit+1 since the remaining suffix after the maxsplitth split is included in the output.
Default value “0”.
![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.
![]() lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
![]() name (optional) : string, name of the node.
name (optional) : string, name of the node.
Output parameters
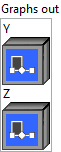
![]() Y (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, tensor of substrings representing the outcome of splitting the strings in the input on the delimiter. Note that to ensure the same number of elements are present in the final rank, this tensor will pad any necessary empty strings.
Y (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, tensor of substrings representing the outcome of splitting the strings in the input on the delimiter. Note that to ensure the same number of elements are present in the final rank, this tensor will pad any necessary empty strings.
![]() Z (heterogeneous) – T3 : object, the number of substrings generated for each input element.
Z (heterogeneous) – T3 : object, the number of substrings generated for each input element.
Type Constraints
tensor(string)) : The input must be a UTF-8 string tensor
T2 in (tensor(string)) : Tensor of substrings.
T3 in (tensor(int64)) : The number of substrings generated.
