-
SOTA
-
Accelerator Toolkit
-
Deep Learning Toolkit
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AlphaDropout
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- ELU
- Exponential
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- GELU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- HardSigmoid
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- Multiply
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- PReLU
- ReLU
- SELU
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Sigmoid
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- Split
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- Substract
- Show All Articles (63) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Exp
- Identity
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- lrfft
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- Shape
- SequenceLength
- Shrink
- Sin
- Sign
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- lslnf
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- Show All Articles (65) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- ConvInteger
- Conv
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Sinh
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLinear
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- LSTM
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- MutiHeadAttention
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- MultiHeadAttention
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (22) Collapse Articles
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Bidirectional
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dense
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- MultiHeadAttention
- LSTM
- PReLU 5D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (21) Collapse Articles
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MultiHeadAttention
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Resume
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- PReLU 4D
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Resume
- Show All Articles (27) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- BatchNormalization
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Computer Vision Toolkit
-
CUDA Toolkit
-
- Resume
- Array size
- Index Array
- Replace Subset
- Insert Into Array
- Delete From Array
- Initialize Array
- Build Array
- Concatenate Array
- Array Subset
- Min & Max
- Reshape Array
- Short Array
- Reverse 1D array
- Shuffle array
- Search In Array
- Split 1D Array
- Split 2D Array
- Rotate 1D Array
- Increment Array Element
- Decrement Array Element
- Interpolate 1D Array
- Threshold 1D Array
- Interleave 1D Array
- Decimate 1D Array
- Transpose Array
- Remove Duplicate From 1D Array
- Show All Articles (11) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- Substract
- Multiply
- Divide
- Quotient & Remainder
- Increment
- Decrement
- Add Array Element
- Multiply Array Element
- Absolute
- Round To Nearest
- Round Toward -Infinity
- Round Toward +Infinity
- Scale By Power Of Two
- Square Root
- Square
- Negate
- Reciprocal
- Sign
- Show All Articles (4) Collapse Articles
MatMulNBits
Description
MatMulNBits performs a matrix multiplication where the right-hand-side matrix (weights) is quantized to N bits.
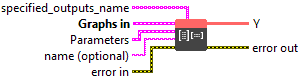
It is a fusion of two operations :
- Linear dequantization of the quantized weights using scale and (optionally) zero-point with formula: dequantized_weight = (quantized_weight – zero_point) * scale
- Matrix multiplication between the input matrix A and the dequantized weight matrix.
The weight matrix is a 2D constant matrix with the input feature count and output feature count specified by attributes ‘K’ and ‘N’. It is quantized block-wise along the K dimension with a block size specified by the ‘block_size’ attribute. The block size must be a power of 2 and not smaller than 16 (e.g., 16, 32, 64, 128). Each block has its own scale and zero-point. The quantization is performed using a bit-width specified by the ‘bits’ attribute, which can take values from 2 to 8.
The quantized weights are stored in a bit-packed format along the K dimension, with each block being represented by a blob of uint8. For example, for 4 bits, the first 4 bits are stored in the lower 4 bits of a byte, and the second 4 bits are stored in the higher 4 bits of a byte.
Input parameters
![]() specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
![]() Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
![]() A (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, the input tensor, not quantized.
A (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, the input tensor, not quantized.![]() B (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, packed uint8 tensor of shape (N, k_blocks, blob_size), where k_blocks = ceil(K / block_size) and blob_size = (block_size * bits / 8). The quantized weights are stored in a bit-packed format along the K dimension, packed within each block_size.
B (heterogeneous) – T2 : object, packed uint8 tensor of shape (N, k_blocks, blob_size), where k_blocks = ceil(K / block_size) and blob_size = (block_size * bits / 8). The quantized weights are stored in a bit-packed format along the K dimension, packed within each block_size.![]() scales (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, per-block scaling factors for dequantization with shape (N, k_blocks) and same data type as input A.
scales (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, per-block scaling factors for dequantization with shape (N, k_blocks) and same data type as input A.![]() zero_points (optional, heterogeneous) – T3 : object, per-block zero point for dequantization. It can be either packed or unpacked: Packed (uint8) format has shape (N, ceil(k_blocks * bits / 8)), and it uses same bit-packing method as Input B. Unpacked (same type as A) format has shape (N, k_blocks). If not provided, a default zero point is used: 2^(bits – 1) (e.g., 8 for 4-bit quantization, 128 for 8-bit).
zero_points (optional, heterogeneous) – T3 : object, per-block zero point for dequantization. It can be either packed or unpacked: Packed (uint8) format has shape (N, ceil(k_blocks * bits / 8)), and it uses same bit-packing method as Input B. Unpacked (same type as A) format has shape (N, k_blocks). If not provided, a default zero point is used: 2^(bits – 1) (e.g., 8 for 4-bit quantization, 128 for 8-bit).![]() g_idx (optional, heterogeneous) – T4 : object, group_idx. This input is deprecated.
g_idx (optional, heterogeneous) – T4 : object, group_idx. This input is deprecated.![]() bias (optional, heterogeneous) – T1 : object, bias to add to result. It should have shape [N].
bias (optional, heterogeneous) – T1 : object, bias to add to result. It should have shape [N].

![]() Parameters : cluster,
Parameters : cluster,
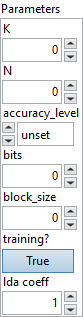
![]() K : integer, input feature dimension of the weight matrix.
K : integer, input feature dimension of the weight matrix.
Default value “0”.![]() N : integer, output feature dimension of the weight matrix.
N : integer, output feature dimension of the weight matrix.
Default value “0”.![]() accuracy_level : enum, the minimum accuracy level of input A, can be: 0(unset), 1(fp32), 2(fp16), 3(bf16), or 4(int8) (default unset). It is used to control how input A is quantized or downcast internally while doing computation, for example: 0 means input A will not be quantized or downcast while doing computation. 4 means input A can be quantized with the same block_size to int8 internally from type T1.
accuracy_level : enum, the minimum accuracy level of input A, can be: 0(unset), 1(fp32), 2(fp16), 3(bf16), or 4(int8) (default unset). It is used to control how input A is quantized or downcast internally while doing computation, for example: 0 means input A will not be quantized or downcast while doing computation. 4 means input A can be quantized with the same block_size to int8 internally from type T1.
Default value “unset”.![]() bits : integer, bit-width used to quantize the weights (valid range: 2~8).
bits : integer, bit-width used to quantize the weights (valid range: 2~8).
Default value “0”.![]() block_size : integer, size of each quantization block along the K (input feature) dimension. Must be a power of two and ≥ 16 (e.g., 16, 32, 64, 128).
block_size : integer, size of each quantization block along the K (input feature) dimension. Must be a power of two and ≥ 16 (e.g., 16, 32, 64, 128).
Default value “0”.![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.![]() lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
![]() name (optional) : string, name of the node.
name (optional) : string, name of the node.
Output parameters
![]() Y (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, tensor. The output tensor has the same rank as the input.
Y (heterogeneous) – T1 : object, tensor. The output tensor has the same rank as the input.
Type Constraints
T1 in (tensor(float), tensor(float16), tensor(bfloat16)) : Constrain input and output types to float tensors.
T2 in (tensor(uint8)) : Constrain quantized weight types to uint8.
T3 in (tensor(uint8), tensor(float), tensor(float16), tensor(bfloat16)) : Constrain quantized zero point types to uint8 or float tensors.
T4 in (tensor(int32)) : the index tensor.
