-
SOTA
-
Accelerator Toolkit
-
Deep Learning Toolkit
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AlphaDropout
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- ELU
- Exponential
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- GELU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- HardSigmoid
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- Multiply
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- PReLU
- ReLU
- SELU
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Sigmoid
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- Split
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- Substract
- Show All Articles (63) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Exp
- Identity
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- lrfft
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- Shape
- SequenceLength
- Shrink
- Sin
- Sign
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- lslnf
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- Show All Articles (65) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- ConvInteger
- Conv
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Sinh
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLinear
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- LSTM
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- MutiHeadAttention
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- MultiHeadAttention
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (22) Collapse Articles
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Bidirectional
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dense
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- MultiHeadAttention
- LSTM
- PReLU 5D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (21) Collapse Articles
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MultiHeadAttention
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Resume
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- PReLU 4D
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Resume
- Show All Articles (27) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- BatchNormalization
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Computer Vision Toolkit
-
CUDA Toolkit
-
- Resume
- Array size
- Index Array
- Replace Subset
- Insert Into Array
- Delete From Array
- Initialize Array
- Build Array
- Concatenate Array
- Array Subset
- Min & Max
- Reshape Array
- Short Array
- Reverse 1D array
- Shuffle array
- Search In Array
- Split 1D Array
- Split 2D Array
- Rotate 1D Array
- Increment Array Element
- Decrement Array Element
- Interpolate 1D Array
- Threshold 1D Array
- Interleave 1D Array
- Decimate 1D Array
- Transpose Array
- Remove Duplicate From 1D Array
- Show All Articles (11) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- Substract
- Multiply
- Divide
- Quotient & Remainder
- Increment
- Decrement
- Add Array Element
- Multiply Array Element
- Absolute
- Round To Nearest
- Round Toward -Infinity
- Round Toward +Infinity
- Scale By Power Of Two
- Square Root
- Square
- Negate
- Reciprocal
- Sign
- Show All Articles (4) Collapse Articles
Multi Input Data by name
Description
Fit (loop-style training) the model with a scheduled learning rate, iterating over multi-input data by name within a Training Session, using a pre-configured learning rate scheduler.
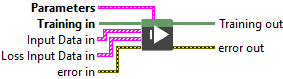
Input parameters
![]() Training in : object, training session.
Training in : object, training session.
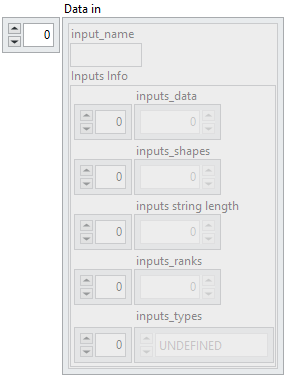
![]() Input Data in : array, is an array of clusters, where each cluster represents a single model input. Each cluster contains metadata and raw data required to describe and pass an input tensor to the model.
Input Data in : array, is an array of clusters, where each cluster represents a single model input. Each cluster contains metadata and raw data required to describe and pass an input tensor to the model.
![]() input_name : string, specifies the identifier of the input. It corresponds to the name given to the input during its creation (via the optional name parameter).
input_name : string, specifies the identifier of the input. It corresponds to the name given to the input during its creation (via the optional name parameter).![]() Inputs Info : cluster
Inputs Info : cluster
![]() inputs_data : array, contains the raw byte representation of the input tensor data, stored as a 1D flattened buffer.
inputs_data : array, contains the raw byte representation of the input tensor data, stored as a 1D flattened buffer.![]() inputs_shapes : array, specifies the shape of the input tensor. Since the data is stored as a flattened 1D buffer, this shape is necessary to reconstruct the original dimensions.
inputs_shapes : array, specifies the shape of the input tensor. Since the data is stored as a flattened 1D buffer, this shape is necessary to reconstruct the original dimensions.![]() inputs string length : array, used when the tensor type is string. If the tensor has shape
inputs string length : array, used when the tensor type is string. If the tensor has shape [5,3], this field contains 15 values, each representing the length of a corresponding string element. This ensures that the actual size of inputs_data is known despite variable string lengths.![]() inputs_ranks : array, indicates the rank of the tensor, i.e. the number of dimensions (Scalar = 0, 1D = 1, 2D = 2, etc.).
inputs_ranks : array, indicates the rank of the tensor, i.e. the number of dimensions (Scalar = 0, 1D = 1, 2D = 2, etc.).![]() inputs_types : array, defines the ONNX tensor type as an enumerated value (e.g. FLOAT, INT64, STRING).
inputs_types : array, defines the ONNX tensor type as an enumerated value (e.g. FLOAT, INT64, STRING).
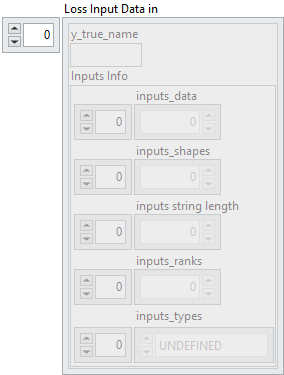
![]() Loss Input Data in : array, is an array of clusters, where each cluster represents a single model input. Each cluster contains metadata and raw data required to describe and pass an input tensor to the model.
Loss Input Data in : array, is an array of clusters, where each cluster represents a single model input. Each cluster contains metadata and raw data required to describe and pass an input tensor to the model.
![]() y_true_name : string, specifies the identifier of the input. It corresponds to the name given to the input during its creation (via the optional name parameter).
y_true_name : string, specifies the identifier of the input. It corresponds to the name given to the input during its creation (via the optional name parameter).![]() Inputs Info : cluster
Inputs Info : cluster
![]() inputs_data : array, contains the raw byte representation of the input tensor data, stored as a 1D flattened buffer.
inputs_data : array, contains the raw byte representation of the input tensor data, stored as a 1D flattened buffer.![]() inputs_shapes : array, specifies the shape of the input tensor. Since the data is stored as a flattened 1D buffer, this shape is necessary to reconstruct the original dimensions.
inputs_shapes : array, specifies the shape of the input tensor. Since the data is stored as a flattened 1D buffer, this shape is necessary to reconstruct the original dimensions.![]() inputs string length : array, used when the tensor type is string. If the tensor has shape
inputs string length : array, used when the tensor type is string. If the tensor has shape [5,3], this field contains 15 values, each representing the length of a corresponding string element. This ensures that the actual size of inputs_data is known despite variable string lengths.![]() inputs_ranks : array, indicates the rank of the tensor, i.e. the number of dimensions (Scalar = 0, 1D = 1, 2D = 2, etc.).
inputs_ranks : array, indicates the rank of the tensor, i.e. the number of dimensions (Scalar = 0, 1D = 1, 2D = 2, etc.).![]() inputs_types : array, defines the ONNX tensor type as an enumerated value (e.g. FLOAT, INT64, STRING).
inputs_types : array, defines the ONNX tensor type as an enumerated value (e.g. FLOAT, INT64, STRING).
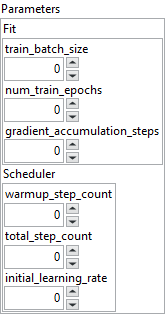
![]() Parameters : cluster
Parameters : cluster
![]() Fit : cluster
Fit : cluster
![]() train_batch_size : integer, number of samples processed per batch during training.
train_batch_size : integer, number of samples processed per batch during training.![]() num_train_epochs : integer, total number of passes over the entire dataset.
num_train_epochs : integer, total number of passes over the entire dataset.![]() gradient_accumulation_steps : integer, number of steps to accumulate gradients before updating the weights.
gradient_accumulation_steps : integer, number of steps to accumulate gradients before updating the weights.
![]() Scheduler : cluster
Scheduler : cluster
![]() warmup_step_count : integer, number of steps during which the learning rate increases linearly from 0 up to the initial_learning_rate.
warmup_step_count : integer, number of steps during which the learning rate increases linearly from 0 up to the initial_learning_rate.![]() total_step_count : integer, total number of training steps for the scheduler. After reaching the initial_learning_rate, the learning rate linearly decays to 0 over the remaining steps.
total_step_count : integer, total number of training steps for the scheduler. After reaching the initial_learning_rate, the learning rate linearly decays to 0 over the remaining steps.![]() initial_learning_rate : float, maximum learning rate reached at the end of the warm‑up phase, before the linear decay begins.
initial_learning_rate : float, maximum learning rate reached at the end of the warm‑up phase, before the linear decay begins.
Output parameters
![]() Training out : object, training session.
Training out : object, training session.
Example
All these exemples are snippets PNG, you can drop these Snippet onto the block diagram and get the depicted code added to your VI (Do not forget to install Deep Learning library to run it).
