-
SOTA
-
Accelerator Toolkit
-
Deep Learning Toolkit
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- AlphaDropout
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- Average
- AvgPool1D
- AvgPool2D
- AvgPool3D
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Concatenate
- Conv1D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- Cropping1D
- Cropping2D
- Cropping3D
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dropout
- Embedding
- Flatten
- ELU
- Exponential
- GaussianDropout
- GaussianNoise
- GlobalAvgPool1D
- GlobalAvgPool2D
- GlobalAvgPool3D
- GlobalMaxPool1D
- GlobalMaxPool2D
- GlobalMaxPool3D
- GRU
- GELU
- Input
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MaxPool1D
- MaxPool2D
- MaxPool3D
- MultiHeadAttention
- HardSigmoid
- LeakyReLU
- Linear
- Multiply
- Permute3D
- Reshape
- RNN
- PReLU
- ReLU
- SELU
- Output Predict
- Output Train
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- SpatialDropout
- Sigmoid
- SoftMax
- SoftPlus
- SoftSign
- Split
- UpSampling1D
- UpSampling2D
- UpSampling3D
- ZeroPadding1D
- ZeroPadding2D
- ZeroPadding3D
- Swish
- TanH
- ThresholdedReLU
- Substract
- Show All Articles (63) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
- Exp
- Identity
- Abs
- Acos
- Acosh
- ArgMax
- ArgMin
- Asin
- Asinh
- Atan
- Atanh
- AveragePool
- Bernouilli
- BitwiseNot
- BlackmanWindow
- Cast
- Ceil
- Celu
- ConcatFromSequence
- Cos
- Cosh
- DepthToSpace
- Det
- DynamicTimeWarping
- Erf
- EyeLike
- Flatten
- Floor
- GlobalAveragePool
- GlobalLpPool
- GlobalMaxPool
- HammingWindow
- HannWindow
- HardSwish
- HardMax
- lrfft
- lsNaN
- Log
- LogSoftmax
- LpNormalization
- LpPool
- LRN
- MeanVarianceNormalization
- MicrosoftGelu
- Mish
- Multinomial
- MurmurHash3
- Neg
- NhwcMaxPool
- NonZero
- Not
- OptionalGetElement
- OptionalHasElement
- QuickGelu
- RandomNormalLike
- RandomUniformLike
- RawConstantOfShape
- Reciprocal
- ReduceSumInteger
- RegexFullMatch
- Rfft
- Round
- SampleOp
- Shape
- SequenceLength
- Shrink
- Sin
- Sign
- Sinh
- Size
- SpaceToDepth
- Sqrt
- StringNormalizer
- Tan
- TfldfVectorizer
- Tokenizer
- Transpose
- UnfoldTensor
- lslnf
- ImageDecoder
- Inverse
- Show All Articles (65) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
- Add
- AffineGrid
- And
- BiasAdd
- BiasGelu
- BiasSoftmax
- BiasSplitGelu
- BitShift
- BitwiseAnd
- BitwiseOr
- BitwiseXor
- CastLike
- CDist
- CenterCropPad
- Clip
- Col2lm
- ComplexMul
- ComplexMulConj
- Compress
- ConvInteger
- Conv
- ConvTranspose
- ConvTransposeWithDynamicPads
- CropAndResize
- CumSum
- DeformConv
- DequantizeBFP
- DequantizeLinear
- DequantizeWithOrder
- DFT
- Div
- DynamicQuantizeMatMul
- Equal
- Expand
- ExpandDims
- FastGelu
- FusedConv
- FusedGemm
- FusedMatMul
- FusedMatMulActivation
- GatedRelativePositionBias
- Gather
- GatherElements
- GatherND
- Gemm
- GemmFastGelu
- GemmFloat8
- Greater
- GreaterOrEqual
- GreedySearch
- GridSample
- GroupNorm
- InstanceNormalization
- Less
- LessOrEqual
- LongformerAttention
- MatMul
- MatMulBnb4
- MatMulFpQ4
- MatMulInteger
- MatMulInteger16
- MatMulIntergerToFloat
- MatMulNBits
- MaxPoolWithMask
- MaxRoiPool
- MaxUnPool
- MelWeightMatrix
- MicrosoftDequantizeLinear
- MicrosoftGatherND
- MicrosoftGridSample
- MicrosoftPad
- MicrosoftQLinearConv
- MicrosoftQuantizeLinear
- MicrosoftRange
- MicrosoftTrilu
- Mod
- MoE
- Mul
- MulInteger
- NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss
- NGramRepeatBlock
- NhwcConv
- NhwcFusedConv
- NonMaxSuppression
- OneHot
- Or
- PackedAttention
- PackedMultiHeadAttention
- Pad
- Pow
- QGemm
- QLinearAdd
- QLinearAveragePool
- QLinearConcat
- QLinearConv
- QLinearGlobalAveragePool
- QLinearLeakyRelu
- QLinearMatMul
- QLinearMul
- QLinearReduceMean
- QLinearSigmoid
- QLinearSoftmax
- QLinearWhere
- QMoE
- QOrderedAttention
- QOrderedGelu
- QOrderedLayerNormalization
- QOrderedLongformerAttention
- QOrderedMatMul
- QuantizeLinear
- QuantizeWithOrder
- Range
- ReduceL1
- ReduceL2
- ReduceLogSum
- ReduceLogSumExp
- ReduceMax
- ReduceMean
- ReduceMin
- ReduceProd
- ReduceSum
- ReduceSumSquare
- RelativePositionBias
- Reshape
- Resize
- RestorePadding
- ReverseSequence
- RoiAlign
- RotaryEmbedding
- ScatterElements
- ScatterND
- SequenceAt
- SequenceErase
- SequenceInsert
- Sinh
- Slice
- SparseToDenseMatMul
- SplitToSequence
- Squeeze
- STFT
- StringConcat
- Sub
- Tile
- TorchEmbedding
- TransposeMatMul
- Trilu
- Unsqueeze
- Where
- WordConvEmbedding
- Xor
- Show All Articles (134) Collapse Articles
-
- Attention
- AttnLSTM
- BatchNormalization
- BiasDropout
- BifurcationDetector
- BitmaskBiasDropout
- BitmaskDropout
- DecoderAttention
- DecoderMaskedMultiHeadAttention
- DecoderMaskedSelfAttention
- Dropout
- DynamicQuantizeLinear
- DynamicQuantizeLSTM
- EmbedLayerNormalization
- GemmaRotaryEmbedding
- GroupQueryAttention
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MicrosoftMultiHeadAttention
- QAttention
- RemovePadding
- RNN
- Sampling
- SkipGroupNorm
- SkipLayerNormalization
- SkipSimplifiedLayerNormalization
- SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss
- SparseAttention
- TopK
- WhisperBeamSearch
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- LSTM
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- MutiHeadAttention
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- MultiHeadAttention
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (22) Collapse Articles
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Bidirectional
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Dense
- Embedding
- LayerNormalization
- GRU
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- MultiHeadAttention
- LSTM
- PReLU 5D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- 1D
- 2D
- 3D
- 4D
- 5D
- 6D
- Scalar
- Show All Articles (21) Collapse Articles
-
-
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- BatchNormalization
- Bidirectional
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Dense
- DepthwiseConv2D
- Embedding
- GRU
- LayerNormalization
- LSTM
- MultiHeadAttention
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Resume
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (12) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- PReLU 4D
- Show All Articles (15) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Accuracy
- BinaryAccuracy
- BinaryCrossentropy
- BinaryIoU
- CategoricalAccuracy
- CategoricalCrossentropy
- CategoricalHinge
- CosineSimilarity
- FalseNegatives
- FalsePositives
- Hinge
- Huber
- IoU
- KLDivergence
- LogCoshError
- Mean
- MeanAbsoluteError
- MeanAbsolutePercentageError
- MeanIoU
- MeanRelativeError
- MeanSquaredError
- MeanSquaredLogarithmicError
- MeanTensor
- OneHotIoU
- OneHotMeanIoU
- Poisson
- Precision
- PrecisionAtRecall
- Recall
- RecallAtPrecision
- RootMeanSquaredError
- SensitivityAtSpecificity
- SparseCategoricalAccuracy
- SparseCategoricalCrossentropy
- SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy
- Specificity
- SpecificityAtSensitivity
- SquaredHinge
- Sum
- TopKCategoricalAccuracy
- TrueNegatives
- TruePositives
- Resume
- Show All Articles (27) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- BatchNormalization
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
- Dense
- Embedding
- AdditiveAttention
- Attention
- MultiHeadAttention
- Conv1D
- Conv2D
- Conv3D
- ConvLSTM1D
- ConvLSTM2D
- ConvLSTM3D
- Conv1DTranspose
- Conv2DTranspose
- Conv3DTranspose
- DepthwiseConv2D
- SeparableConv1D
- SeparableConv2D
- LayerNormalization
- PReLU 2D
- PReLU 3D
- PReLU 4D
- PReLU 5D
- Bidirectional
- GRU
- LSTM
- RNN (GRU)
- RNN (LSTM)
- RNN (SimpleRNN)
- SimpleRNN
- BatchNormalization
- Show All Articles (14) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Computer Vision Toolkit
-
CUDA Toolkit
-
- Resume
- Array size
- Index Array
- Replace Subset
- Insert Into Array
- Delete From Array
- Initialize Array
- Build Array
- Concatenate Array
- Array Subset
- Min & Max
- Reshape Array
- Short Array
- Reverse 1D array
- Shuffle array
- Search In Array
- Split 1D Array
- Split 2D Array
- Rotate 1D Array
- Increment Array Element
- Decrement Array Element
- Interpolate 1D Array
- Threshold 1D Array
- Interleave 1D Array
- Decimate 1D Array
- Transpose Array
- Remove Duplicate From 1D Array
- Show All Articles (11) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Resume
- Add
- Substract
- Multiply
- Divide
- Quotient & Remainder
- Increment
- Decrement
- Add Array Element
- Multiply Array Element
- Absolute
- Round To Nearest
- Round Toward -Infinity
- Round Toward +Infinity
- Scale By Power Of Two
- Square Root
- Square
- Negate
- Reciprocal
- Sign
- Show All Articles (4) Collapse Articles
ConvTranspose
Description
The convolution transpose operator consumes an input tensor and a filter, and computes the output.
If the pads parameter is provided the shape of the output is calculated via the following equation :
output_shape = stride * (input_size – 1) + output_padding + ((kernel_shape – 1) * dilations + 1) – pads[start_i] – pads[end_i]
output_shape can also be explicitly specified in which case pads values are auto generated using these equations :
total_padding = stride * (input_size – 1) + output_padding + ((kernel_shape – 1) * dilations + 1) – output_shape If (auto_pads == SAME_UPPER): pads[start_i] = total_padding/2; pads[end_i] = total_padding – (total_padding/2) Else: pads[start_i] = total_padding – (total_padding/2); pads[end_i] = (total_padding/2).
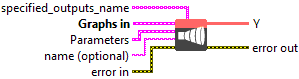
Input parameters
![]() specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
specified_outputs_name : array, this parameter lets you manually assign custom names to the output tensors of a node.
![]() Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
Graphs in : cluster, ONNX model architecture.
![]() X (heterogeneous) – T : object, input data tensor from previous layer; has size (N x C x H x W), where N is the batch size, C is the number of channels, and H and W are the height and width. Note that this is for the 2D image. Otherwise the size is (N x C x D1 x D2 … x Dn).
X (heterogeneous) – T : object, input data tensor from previous layer; has size (N x C x H x W), where N is the batch size, C is the number of channels, and H and W are the height and width. Note that this is for the 2D image. Otherwise the size is (N x C x D1 x D2 … x Dn).![]() W (heterogeneous) – T : object, the weight tensor that will be used in the convolutions; has size (C x M/group x kH x kW), where C is the number of channels, and kH and kW are the height and width of the kernel, and M is the number of feature maps. For more than 2 dimensions, the weight shape will be (C x M/group x k1 x k2 x … x kn), where (k1 x k2 x … x kn) is the dimension of the kernel. The number of channels in the output should be equal to W.shape[1] * group (assuming zero based indices of the shape array).
W (heterogeneous) – T : object, the weight tensor that will be used in the convolutions; has size (C x M/group x kH x kW), where C is the number of channels, and kH and kW are the height and width of the kernel, and M is the number of feature maps. For more than 2 dimensions, the weight shape will be (C x M/group x k1 x k2 x … x kn), where (k1 x k2 x … x kn) is the dimension of the kernel. The number of channels in the output should be equal to W.shape[1] * group (assuming zero based indices of the shape array).![]() B (optional, heterogeneous) – T : object, optional 1D bias to be added to the convolution, has size of M.
B (optional, heterogeneous) – T : object, optional 1D bias to be added to the convolution, has size of M.

![]() Parameters : cluster,
Parameters : cluster,
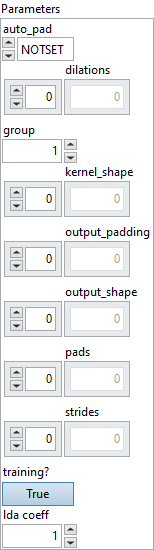
![]() auto_pad : enum, auto_pad must be either NOTSET, SAME_UPPER, SAME_LOWER or VALID. Where default value is NOTSET, which means explicit padding is used. SAME_UPPER or SAME_LOWER mean pad the input so that
auto_pad : enum, auto_pad must be either NOTSET, SAME_UPPER, SAME_LOWER or VALID. Where default value is NOTSET, which means explicit padding is used. SAME_UPPER or SAME_LOWER mean pad the input so that output_shape = input_shape * strides for each axis i. The padding is split between the two sides equally or almost equally (depending on whether it is even or odd). In case the padding is an odd number, the extra padding is added at the end for SAME_UPPER and at the beginning for SAME_LOWER.
Default value “NOTSET”.![]() dilations : array, dilation value along each spatial axis of the filter. If not present, the dilation defaults to 1 along each spatial axis.
dilations : array, dilation value along each spatial axis of the filter. If not present, the dilation defaults to 1 along each spatial axis.
Default value “empty”.![]() group : integer, number of groups input channels and output channels are divided into.
group : integer, number of groups input channels and output channels are divided into.
Default value “1”.![]() kernel_shape : array, the shape of the convolution kernel. If not present, should be inferred from input W.
kernel_shape : array, the shape of the convolution kernel. If not present, should be inferred from input W.
Default value “empty”.![]() output_padding : array, additional elements added to the side with higher coordinate indices in the output. Each padding value in “output_padding” must be less than the corresponding stride/dilation dimension. By default, this attribute is a zero vector. Note that this attribute doesn’t directly affect the computed output values. It only controls the selection of the computed values, so changing this attribute only adds or removes output elements. If “output_shape” is explicitly provided, “output_padding” does not contribute additional size to “output_shape” but participates in the computation of the needed padding amount. This is also called adjs or adjustment in some frameworks.
output_padding : array, additional elements added to the side with higher coordinate indices in the output. Each padding value in “output_padding” must be less than the corresponding stride/dilation dimension. By default, this attribute is a zero vector. Note that this attribute doesn’t directly affect the computed output values. It only controls the selection of the computed values, so changing this attribute only adds or removes output elements. If “output_shape” is explicitly provided, “output_padding” does not contribute additional size to “output_shape” but participates in the computation of the needed padding amount. This is also called adjs or adjustment in some frameworks.
Default value “empty”.![]() output_shape : array, the shape of the output can be explicitly set which will cause pads values to be auto generated. If output_shape is specified pads values are ignored. See doc for details for equations to generate pads. Note that the output_shape attribute value should not include dimensions for batch size and channels, which are automatically inferred.
output_shape : array, the shape of the output can be explicitly set which will cause pads values to be auto generated. If output_shape is specified pads values are ignored. See doc for details for equations to generate pads. Note that the output_shape attribute value should not include dimensions for batch size and channels, which are automatically inferred.
Default value “empty”.![]() pads : array, padding for the beginning and ending along each spatial axis, it can take any value greater than or equal to 0. The value represent the number of pixels added to the beginning and end part of the corresponding axis.
pads : array, padding for the beginning and ending along each spatial axis, it can take any value greater than or equal to 0. The value represent the number of pixels added to the beginning and end part of the corresponding axis. pads format should be as follow [x1_begin, x2_begin…x1_end, x2_end,…], where xi_begin the number of pixels added at the beginning of axis i and xi_end, the number of pixels added at the end of axis i. This attribute cannot be used simultaneously with auto_pad attribute. If not present, the padding defaults to 0 along start and end of each spatial axis.
Default value “empty”.![]() strides : array, stride along each spatial axis. If not present, the stride defaults to 1 along each spatial axis.
strides : array, stride along each spatial axis. If not present, the stride defaults to 1 along each spatial axis.
Default value “empty”.![]() training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
training? : boolean, whether the layer is in training mode (can store data for backward).
Default value “True”.![]() lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
lda coeff : float, defines the coefficient by which the loss derivative will be multiplied before being sent to the previous layer (since during the backward run we go backwards).
Default value “1”.
![]() name (optional) : string, name of the node.
name (optional) : string, name of the node.
Output parameters
![]() Y (heterogeneous) – T : object, output data tensor that contains the result of the convolution. The output dimensions are functions of the kernel size, stride size, pad lengths and group count. The number of channels in the output should be equal to W.shape[1] * group (assuming zero based indices of the shape array).
Y (heterogeneous) – T : object, output data tensor that contains the result of the convolution. The output dimensions are functions of the kernel size, stride size, pad lengths and group count. The number of channels in the output should be equal to W.shape[1] * group (assuming zero based indices of the shape array).
Type Constraints
tensor(double), tensor(float), tensor(float16)) : Constrain input and output types to float tensors.